
Expert Pediatric Orthopaedic Care

Expert Pediatric Orthopaedic Care
Pediatric Orthopaedic Urgent Care
Skip the ER and walk in for essential urgent and trauma medical care for fractures, dislocations, sprains, strains and other injuries, from medical experts focused exclusively on kids.
Minimize your waiting room time – save your spot now.
Walk-ins welcome. No appointment necessary.
Monday - Friday: 8am - 4pm
Closed: Saturday and Sunday
(213) 742-1162
403 West Adams Boulevard
Los Angeles, CA 90007

Walk-ins welcome. No appointment necessary.
Urgent Care Registration Form - EnglishUrgent Care Registration Form - Spanish
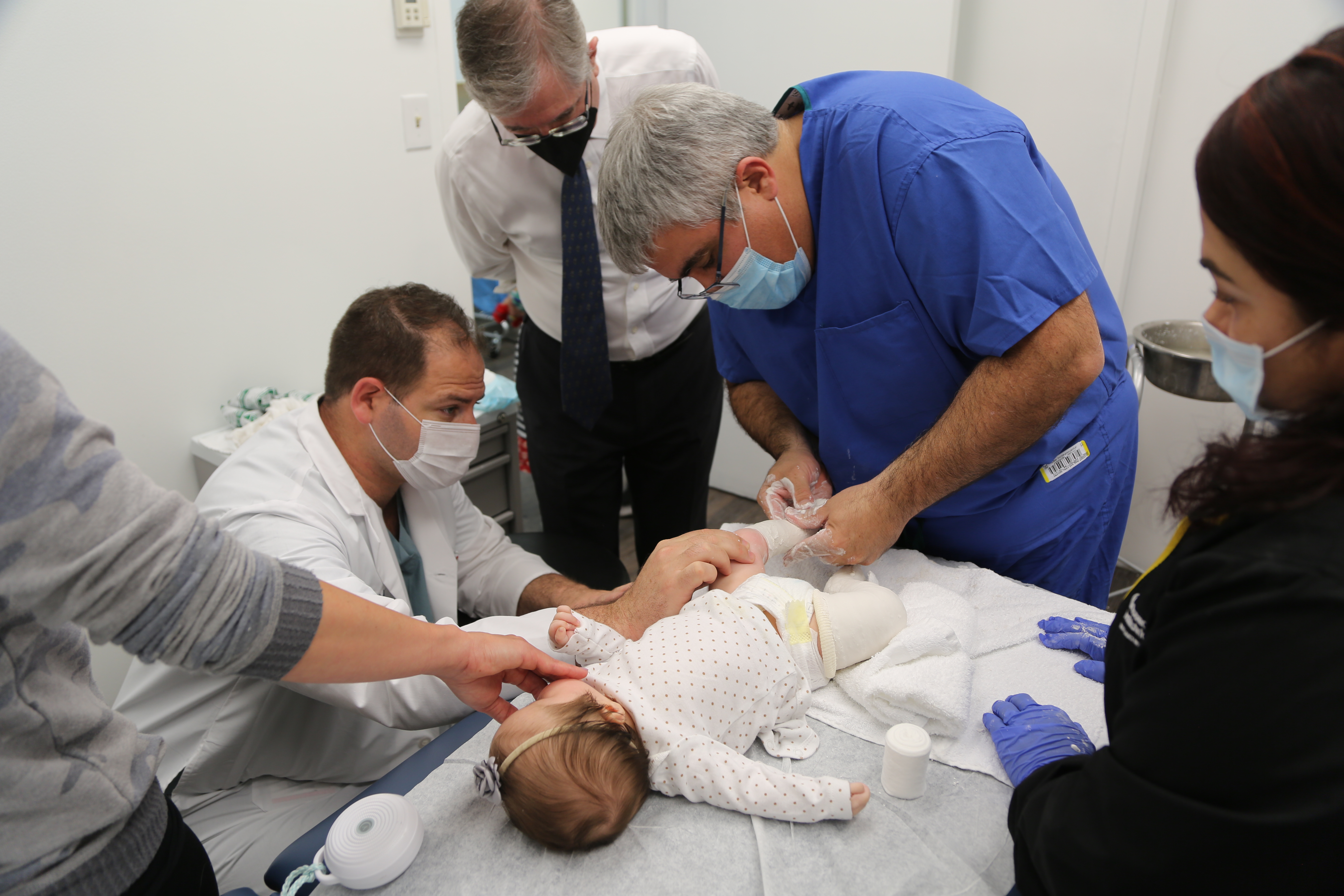
Patient Care is our Priority
Our mission is to provide exceptional care for children and their families.
LuskinOIC's exclusive dedication to pediatric orthopedics has established it as the primary choice for a wide range of issues, including sports and playground injuries, fractures, and even the most uncommon musculoskeletal disorders.

Meet Our Doctors
Our expert team of physicians help children get back to smiles, fun and feeling well again.

Unlocking healthcare equity for California’s children.
LuskinOIC is a nonprofit that depends on the philanthropic support of our community. Your generosity sustains innovative, family-centered patient care, fulfilling LuskinOIC's mission to safeguard children's health and ensure no child is turned away.
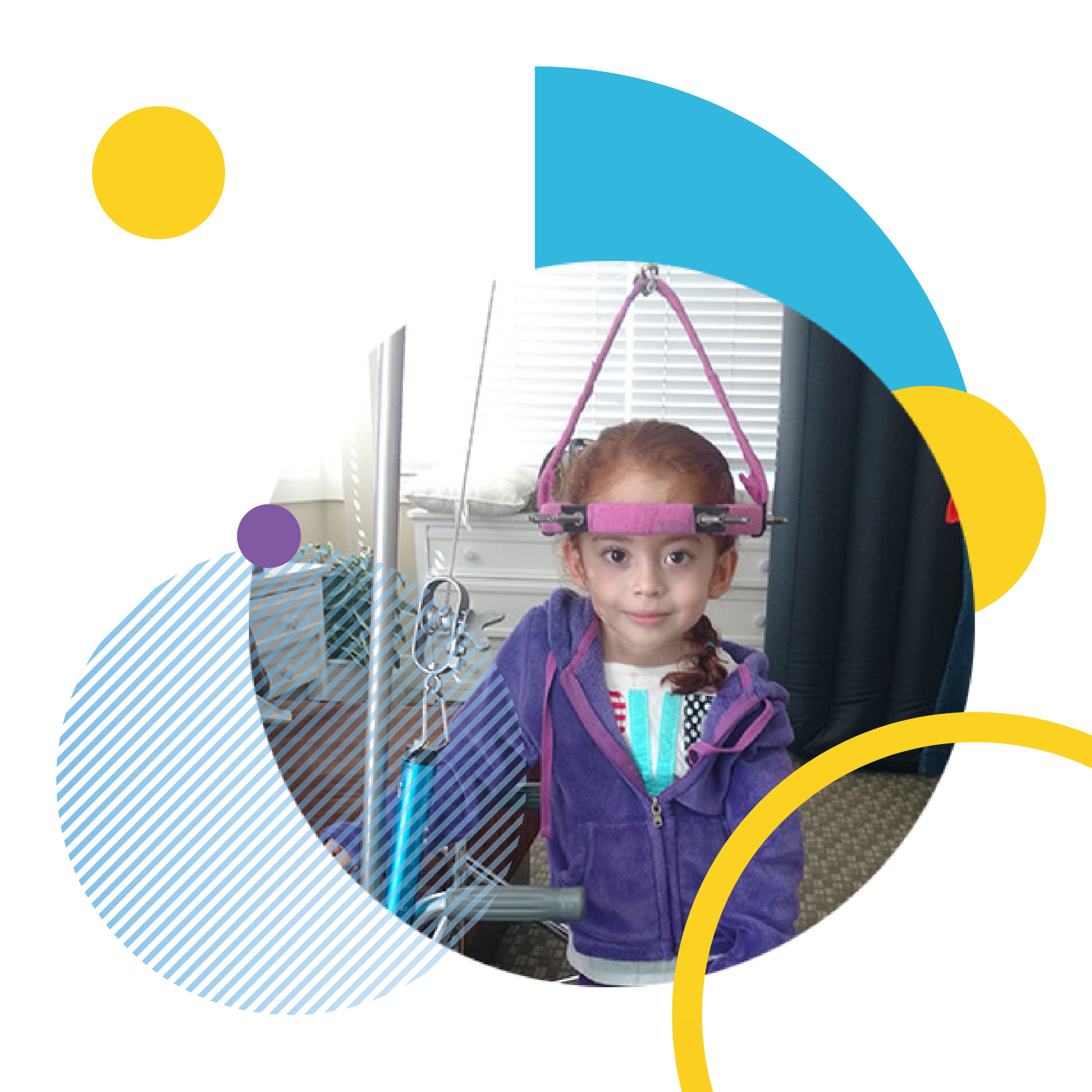

Ivanna's Story
Imagine that your four year old princess has to wear a “crown,” which in reality is a medical device that must stay attached to her skull for 15 hours a day. Ivanna has severe scoliosis, three missing ribs and a dislocated heart. Her red hair is covered with a halo she calls her “Corona de Princesa” – her Princess Crown. Wearing it prepares her for the coming surgeries she will have at LuskinOIC, which will help her stand straighter and breathe easier as she grows.
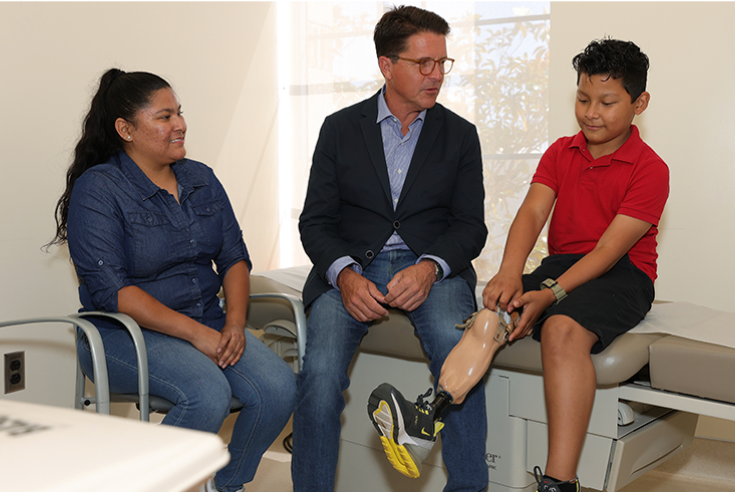

Our Patient Ambassador is front page news!
The LA Times profiled our Patient Ambassador Efrain on the front page of the Friday, March 25th edition.
OUR RESEARCH CENTERS

Downtown LA
J. Vernon Luck SR., MD Research Center
The J. Vernon Luck, Sr., MD Orthopaedic Research Center is located on the Downtown Campus of Orthopaedic Institute for Children, founded as Orthopaedic Hospital in 1911. The Research Center was dedicated to J. Vernon Luck, Sr., M.D., in 1986. The JVL Research Center is internationally recognized for advances in implant performance, including wear, fixation, retrieval analysis, and clinical outcome, as well as fracture, healing and repair.
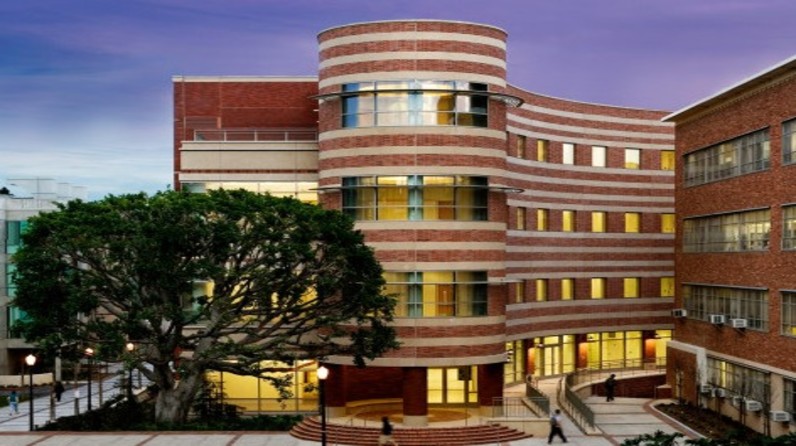

UCLA/Westwood
Orthopaedic Hospital Research Center
It is here that the research activities of Luskin Orthopaedic Institute for Children and UCLA combine to create the largest collaborative and coordinated orthopaedic research effort in the United States. The partnership enables OIC to greatly expand its musculoskeletal research activities to explore and develop new technologies for the discipline of orthopaedic surgery, in addition to new developments in gene therapy, musculoskeletal oncology, tissue engineering and biomedical engineering.

We’re the FIRST medical facility on the West Coast to be KultureCity certified as “sensory inclusive”
LuskinOIC has obtained a certification to better support individuals with sensory sensitivities, commonly associated with conditions like autism, dementia, and PTSD. The primary challenges for such individuals often include sensitivity to overstimulation and noise, particularly in healthcare environments. This certification equips LuskinOIC to offer a more comfortable and accommodating experience for patients with sensory sensitivities during their medical visits. Families planning a visit can use the free KultureCity App to access information on available sensory features and how to utilize them. The app also includes a Social Story, providing a preview of what to expect at LuskinOIC.





